Atualizado em 11/11/2024 07:26

Conversely, a rising operating ratio indicates costs are outpacing revenues and profitability is contracting over time – a potential red flag for future earnings power. The operating Ratio is calculated by dividing total operating expenses by net sales or revenues. Operating expenses include cost of goods sold, selling, general and administrative costs, depreciation, and other operating costs. An operating ratio of less than 100% means the company is generating operating profits, while a ratio above 100% indicates operating losses. An operating ratio is likely to be negative if a company’s operating expenses exceed its revenues, indicating poor profitability.
Total Asset Turnover
This analysis provides crucial insight into the risks and opportunities facing the business. The operating Ratio will vary significantly between industries based on the business model. For example, software companies will typically have much higher margins and lower operating ratios than airlines. As such, the operating Ratio is best used to compare competitors in the same sector as opposed to being used to compare across industries.
Related AccountingTools Courses
Comparing the ratios over time to see how it changes will also reveal any trends. The total operating expenses consist of two components, the cost of goods sold and operating expenses. Return on equity ratio is a profitability ratio which reflects how profitable companies are in relation to their shareholders’ investment. It shows how much money returns to the owners for each dollar invested by them, which enables investors to determine whether it would be worthwhile investing more funding into the company. Solvency indicates your company’s ability to meet its obligations on an ongoing basis, not just in the short term.
Understanding the Operating Margin
Total sales or revenue usually appears at the top of an income statement as the sum total that an organization generates. Liquidity describes whether or not your company can quickly convert its assets into cash to meet its short-term financial obligations. A highly liquid company has ample cash or assets that can be easily sold without a significant loss in value. Rise in the value of the operating ratio is indicative of the decline in the efficiency. The cost of goods sold components consist of factors like opening stock, direct expenses, manufacturing expenses and closing stock. If the company was able to negotiate better prices with its suppliers, reducing its COGS to $500,000, then it would see an improvement in its operating margin to 50%.
Limitations of the Operating Margin
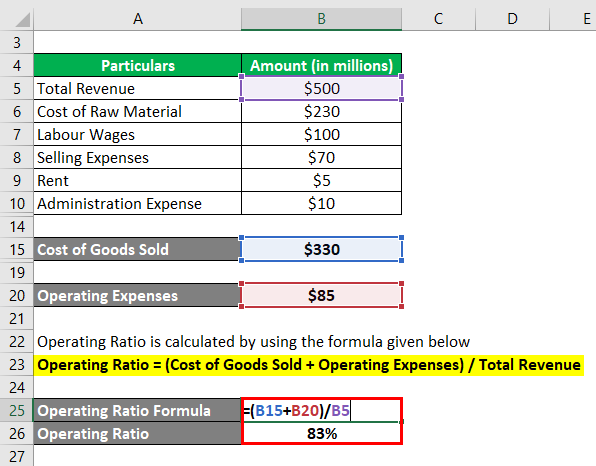
The cost of goods sold is added to operating expenses to determine the operating ratio. Return on investment, or ROI, measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. It is a key indicator of how efficiently an investment is generating returns. Coupled with the days of sales outstanding, this measure can be used to calculate the cash conversion cycle. The cash conversion cycle shows how quickly a firm converts its investment in inventory into cash.
- Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- However, it is possible for a company’s operating Ratio to exceed 100%.
- Companies have some leeway in classifying costs as operating expenses or not.
- She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more.
Operating expenses
For example, a company running at a 20% operating ratio is able to convert five rupees of revenue into four rupees of contribution towards fixed expenses and profit. This 20% ratio indicates consistency in the operating leverage of the company if it remains constant over time. The business is exhibiting consistent conversion of sales growth into earnings growth.
When it comes to managing finances effectively, understanding key metrics and ratios can make a significant difference. Whether you’re a business owner, an investor, or even a finance enthusiast, knowing how to calculate and interpret the operating ratio can help you gauge the operational efficiency and profitability of a company. In this article, we will explore the definition of operating ratio and provide you with a simple formula for calculating it. As with any financial metric, the operating ratio should be monitored over multiple reporting periods to determine if a trend is present. Companies sometimes can cut costs in the short term thus inflating their earnings temporarily.
An investor has to weigh Costco’s operational efficiency against Walmart’s higher margins, pricing power, scale, and omnichannel presence. Costco’s consistently low topic no 458 educator expense deduction reflects a lean and member-driven warehouse model, which has helped it outperform other retailers. However, prudent investments and management choices are equally critical. High or unstable ratios raise doubts over a company’s ability to repay loans with operating income.
Cutting too many costs can also lead to undesirable outcomes, including losing skilled workers, shifting to inferior materials, or other losses in quality. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
It suggests operating efficiency is deteriorating, and there is escalating pressure on margins and earnings. As the operating Ratio climbs upwards, it means a growing chunk of revenue is being consumed by operating expenses rather than turned into profit. In other words, the company is spending more to operate and maintain the business in relation to the top-line revenues coming in the door. However, operating expenses also rose sharply by 74.2% to Rs 4,32,976 crores.
A consistently low or declining operating ratio indicates a company is becoming more efficient at controlling expenses and generating profits from its operations. This reflects positively on management’s ability to run the business efficiently and usually leads to a higher stock valuation. On the other hand, a high or increasing operating ratio suggests inefficient operations and excessive spending, which raises concerns over the company’s profitability. The operating Ratio is calculated by dividing operating expenses by net sales or revenue. Operating expenses include the cost of goods sold, selling, general and administrative expenses, depreciation, and other operating expenditures.
